Testosterone plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, especially in men. It’s commonly associated with libido, muscle mass, and energy levels. As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, prompting interest in ways to boost production through diet. Nutrition and lifestyle have a significant impact on hormone levels. Certain foods are recognized for their potential to increase testosterone, supporting endocrine health and providing men with a natural method to maintain their hormonal balance. Understanding these foods and incorporating them into one’s diet could be an important aspect of managing testosterone levels.
While there’s no magic food that can completely overhaul testosterone levels overnight, a balanced diet rich in specific nutrients may help support the body’s testosterone production. Research suggests a diet that includes lean proteins, essential fatty acids, and certain vitamins and minerals can contribute to hormonal health. For instance, zinc and vitamin D have been linked to testosterone production, and foods such as fatty fish, leafy greens, and fortified products are excellent sources.
Key Takeaways
- Nutritional choices significantly affect testosterone levels, particularly in men.
- A balanced diet with particular nutrients supports the body’s natural testosterone production.
- Hormonal health can be optimized through focused dietary strategies, without reliance on supplementation.
Fundamentals of Testosterone and Diet
Testosterone is a vital male sex hormone that plays a crucial role in muscle development, bone density, and libido. Dietary choices can significantly influence testosterone levels. It is crucial for individuals to focus on proper nutrition to maintain optimal testosterone production.
Key Nutrients Influencing Testosterone:
- Fats: A certain amount of dietary fat is essential for testosterone synthesis. Studies have shown that men consuming diets rich in healthy fats may have higher testosterone levels.
- Vitamins and minerals: Vitamins such as D and B, as well as minerals like zinc and magnesium, are considered essential in testosterone production. Foods rich in these micronutrients are integral to supporting hormonal health.
Balanced Diet for Optimizing Testosterone:
Sufficient calorie consumption and a balanced diet, comprising proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, aid in sustaining normal testosterone levels. Diets that are too restrictive in calories or nutrients may lead to a decrease in testosterone.
- Proteins: crucial for tissue repair and growth, contributing indirectly to hormonal balance.
- Carbohydrates: maintain overall energy levels, supporting endocrine function.
- Fats: especially those rich in omega-3s, are associated with hormone production.
Anecdotal evidence suggests that individuals who integrate a diverse range of nutrient-dense foods often report better overall health, which may correlate to balanced hormone levels. Furthermore, those engaging in regular physical activity alongside a nutritive diet may observe a notable enhancement in their testosterone levels.
Incorporating specific foods that increase the bioavailability of testosterone when taken with meals or ensuring diet composition that efficiently increases absorption can make a significant difference. It’s recommended to combine diet with lifestyle adjustments to promote not only testosterone health but overall well-being.
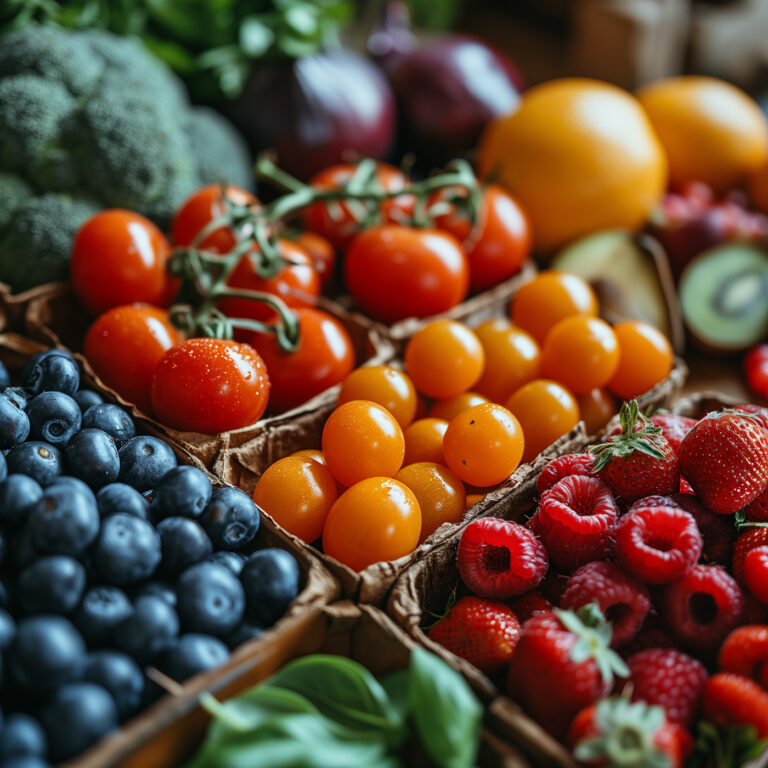
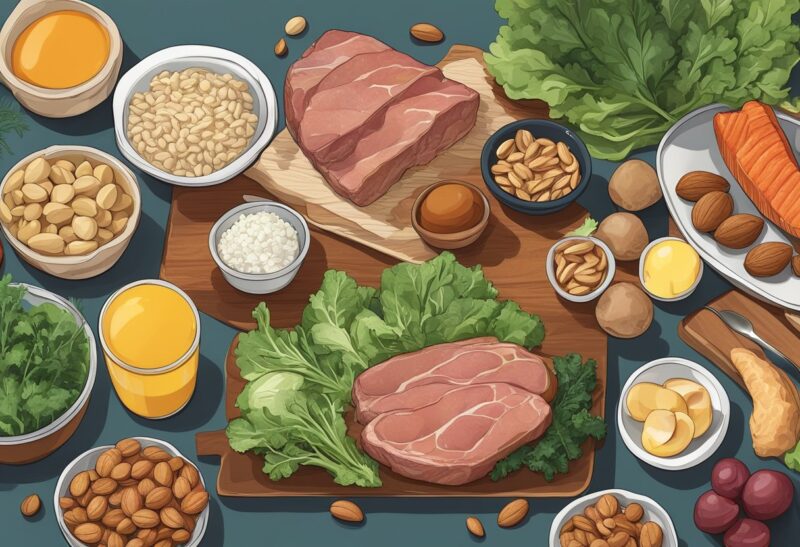
Top Testosterone-Boosting Foods
Testosterone is crucial for muscle growth, bone density, and overall health. Specific foods can aid in increasing testosterone naturally, contributing to improved fertility, sex drive, and sperm production.
Meats and Proteins
Meats, particularly red meat, are rich in proteins and essential nutrients that can support testosterone levels. Eggs are a versatile source, providing vitamin D, which is linked to testosterone production. A friend mentioned that since he started incorporating eggs into his breakfast, he’s felt more vigorous throughout the day.
Seafood Varieties
Oysters lead this category as they’re high in zinc, an essential mineral for testosterone production and male fertility. Fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel are abundant in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, which can help support testosterone levels.
Vegetables and Leafy Greens
Vegetables like spinach and kale come packed with magnesium, a nutrient that has been associated with higher testosterone levels. An acquaintance who is a nutritionist always emphasizes how leafy green vegetables are a non-negotiable part of a hormone-balancing diet.
Fruits and Seeds
Fruits like pomegranates have been found to boost testosterone levels and improve sexual performance and fertility. Seeds, especially those from pumpkins and sunflower, are known for their high zinc content.
Nuts and Legumes
Legumes such as beans and lentils contain zinc and plant-based proteins that can support hormone levels. Nuts, particularly Brazil nuts, are not only rich in healthy fats but also in selenium, a mineral linked to increased testosterone.
Healthy Fat Sources
Olive oil and avocados have monounsaturated fats that can lead to an increase in testosterone levels. Many dieticians recommend olive oil as a healthy fat choice for cooking and dressings due to its health benefits, including hormone health.
Vitamins and Minerals Impact on Testosterone
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0zn54yKd4FU&embed=true
Key nutrients play a crucial role in hormone production, especially in males. Vitamins and minerals such as zinc, vitamin D, magnesium, selenium, and boron are essential for maintaining optimal testosterone levels.
Zinc and Its Role in Hormone Production
Zinc is a vital micronutrient that is directly linked to hormone production, including testosterone. Oysters are not only a well-known aphrodisiac but also the highest natural source of zinc. The consumption of seeds like pumpkin seeds can contribute significantly to the daily zinc requirement which supports the synthesis of testosterone.
Vitamin D: Sunshine and More
Vitamin D, often referred to as the sunshine vitamin, is another vital nutrient that has been shown to influence testosterone levels in men. While direct sunlight exposure is a primary source, dietary sources such as fortified milk can also help in maintaining adequate vitamin D levels, thereby supporting hormone health.
Magnesium, Selenium, and Boron
- Magnesium is a mineral popular for its numerous health benefits, including its contribution to testosterone production. Regular consumption of magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens and nuts can help maintain these levels.
- Selenium, a trace mineral found in a variety of foods such as Brazil nuts and seeds, plays a part in the production of testosterone.
- Boron, while only needed in trace amounts, has been linked to the bodies’ ability to produce and use testosterone effectively. It can be found in foods like avocados and nuts.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Testosterone
Testosterone levels in men are influenced by various lifestyle factors, including exercise, stress management, and diet. These factors can play a significant role in maintaining or improving hormone balance.
Exercise’s Influence on Hormone Levels
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and resistance training are known to effectively increase testosterone production and muscle mass when practiced regularly. A study showed that men engaging in consistent resistance training sessions experienced substantial gains in testosterone levels.
The Impact of Stress and Sleep
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which inversely affects testosterone. Moreover, adequate sleep is vital as poor sleep quality can lower testosterone levels. Supporting this, research has linked full, restorative sleep cycles with optimal hormone balance, directly influencing one’s mood and energy.
Dietary Habits and Their Consequences
Foods high in saturated and trans fats are linked with lower testosterone levels. Conversely, diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids have been associated with the support of testosterone production. The consequences of obesity are also clear; excess body fat, particularly around the waist, can lead to hormonal imbalances and reduced libido. It’s important to limit alcohol intake and processed foods to maintain heart health and manage body weight effectively.
Understanding and Addressing Low Testosterone
Effective management of low testosterone requires an understanding of its symptoms, causes, and interventions. This section delves into the specifics of identifying, addressing, and preventing this hormonal deficiency.
Symptoms and Indicators
Low testosterone levels manifest in a variety of physical and emotional symptoms. Men may experience:
- Decreased libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Affect on mood such as irritability or depression
- Reduced muscle mass and strength
- Increased body fat, sometimes specifically overweight or obesity
These symptoms may be markers for hypogonadism, a condition wherein the body doesn’t produce enough testosterone.
Potential Causes and Health Implications
Causes of low testosterone can range from genetic conditions to lifestyle factors. Some potential causes include:
- Hypogonadism, either present from birth or developing later in life
- Certain medications
- Health concerns such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer
- Exposure to endocrine disruptors like BPA
The health implications of low testosterone are substantial, potentially affecting fertility due to altered sperm motility, and contributing to the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Modern Interventions and Treatments
When addressing testosterone deficiency, the following interventions and treatments are commonly used:
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): Increases testosterone levels, improving symptoms but requires careful medical monitoring.
- Medications: Some drugs stimulate the body to produce more testosterone.
- Supplements: Certain over-the-counter products claim to support testosterone production.
However, one should approach treatments with caution due to potential side effects and always seek a healthcare provider’s guidance.
Preventative Measures and Early Detection
Early detection through routine blood tests can help manage the risk of low testosterone. Lifestyle measures for prevention include:
- Maintaining a healthy diet and nutrition
- Regular exercise
- Avoiding substances like BPA
These practices contribute to overall health and can help maintain optimal testosterone levels.
Optimizing Diet for Testosterone Maintenance
Maintaining optimal testosterone levels is largely influenced by diet. The key is to focus on a balanced intake of nutrients that support hormonal health.
Creating a Balanced Testosterone-Friendly Diet
For individuals aiming to sustain their testosterone levels, incorporating protein-rich foods is essential. Protein supports muscle health, which, in turn, can aid in maintaining healthy testosterone levels. One should concentrate on lean proteins, including grass-fed beef, chicken, and eggs, as they are pivotal for muscle building and repair without excessive saturated fat. Fatty fish, like salmon and mackerel, provide omega-3 fatty acids, which are considered healthy fats necessary for hormone production.
A diet rich in vegetables and fiber is beneficial as well. Vegetables like spinach, Swiss chard, and kale are high in magnesium, a mineral that is associated with positive impacts on testosterone levels. The fiber found in these vegetables, and in other sources like whole grains, assists in stabilizing blood sugar levels, which can help mitigate hormonal imbalances.
Vitamins play a crucial role as well. Vitamin D, which can be obtained through exposure to sunlight or by eating fortified foods and fatty fish, has been linked to testosterone production. Zinc, found in pumpkin seeds and oysters, is also vital for healthy testosterone levels.
Foods and Substances to Avoid
To support testosterone levels, there are certain substances individuals should minimize or avoid. Alcohol consumption in excessive amounts is known to have a negative impact on testosterone. Even moderate drinking can interfere with the body’s ability to maintain optimal hormone levels.
High sugar intake, especially from processed foods, can lead to a spike in insulin and subsequent low testosterone levels. Similarly, diets high in trans fats, which are often found in baked goods and fried foods, can diminish testosterone. It’s advisable for individuals to read nutrition labels carefully to avoid these unhealthy fats.
In summary, a balanced diet that prioritizes lean proteins, healthy fats, and nutrient-dense vegetables while minimizing alcohol, sugar, and trans fats can contribute significantly to maintaining healthy testosterone levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
This subsection aims to address common inquiries on how certain foods and lifestyle choices can naturally influence testosterone levels.
What are the top testosterone-boosting foods?
Certain foods have been linked to increased testosterone production. Foods high in vitamin D and zinc, such as oysters and fatty fish like salmon, are known to support testosterone synthesis. The inclusion of lean meats can also be beneficial due to their high protein content.
How can one quickly elevate their testosterone levels naturally?
A quick elevation in testosterone levels can be supported by consuming foods high in healthy fats, such as avocados and nuts. Engaging in regular strength training and getting adequate sleep each night also contribute to quicker natural increases.
Which specific fruits are known for increasing testosterone?
Fruits like pomegranates and bananas are known to have a positive effect on testosterone levels. Pomegranates, in particular, contain antioxidants that can support heart health and testosterone production.
Are there any vegetarian foods that effectively boost testosterone?
Vegetarian foods that can help boost testosterone include beans, lentils, and other legumes that provide necessary proteins and nutrients. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower can also help due to their content of compounds that potentially lower estrogen levels.
Can dietary choices impact both testosterone and estrogen levels?
Yes, dietary choices can affect both testosterone and estrogen levels. For instance, foods rich in phytoestrogens, like soy products, may influence estrogen, while those high in certain fats can impact testosterone.
What exercises complement dietary efforts in boosting testosterone?
Strength training, especially exercises like squats and deadlifts, effectively complements dietary efforts in boosting testosterone. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) can also increase testosterone levels when combined with a balanced diet.
Related Posts:
- 5 Best Cheap Drawing Tablets for Beginners 2024: Top Choices
- Instant Pot Settings & Buttons Explained: Your Guide…
- 18 Types of Ladybugs Which You Should Know About
- Most Dangerous States in the US (2024): A Safety Overview
- Nvidia Surpasses Apple to Become World's Second Most…
- What Are the Most Popular Sports in The World in 2024?