Apple’s presence in the global market is undeniable. With its innovative products and strategic marketing, the tech giant has established a significant foothold in various regions, including Asia.
This article explains Apple’s sales performance in Asia, drawing insights from recent statistics and offering a comprehensive understanding of the brand’s influence in this vast and diverse continent.
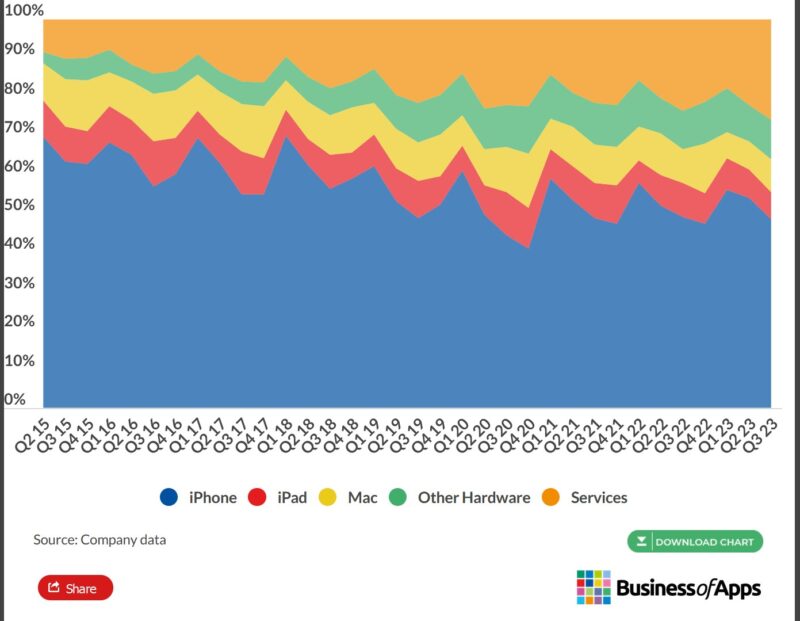
Global Sales
Apple revenue by region 2015 to 2022 ($bn)
| Year | Americas |
Europe |
China |
Japan |
Rest of Asia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 93.8 | 50.3 | 58.7 | 15.7 | 15 |
| 2016 | 86.6 | 49.8 | 48.5 | 16.9 | 13.6 |
| 2017 | 96.6 | 54.9 | 51.6 | 15.3 | 14.1 |
| 2018 | 112 | 62.4 | 51.9 | 21.7 | 17.4 |
| 2019 | 116.9 | 60.2 | 43.6 | 21.5 | 17.8 |
| 2020 | 124.5 | 68.6 | 40.3 | 21.4 | 19.6 |
| 2021 | 153.3 | 89.3 | 68.3 | 28.4 | 26.3 |
| 2022 | 169.6 | 95.1 | 74.2 | 25.9 | 29.3 |
Source: Company data
Apple, a tech behemoth, has consistently demonstrated its ability to dominate markets worldwide. The Americas, for instance, stand as Apple’s most significant regional market, with net sales reaching a staggering 35.38 billion U.S. dollars in Q3 of the fiscal year 2024. Europe and Greater China follow closely, marking themselves as other major markets.
- U.S. Dominance: The substantial revenue from the Americas can be attributed to its robust performance in its home market, the United States. The U.S. alone accounts for over 43% of net sales, further solidified by the high concentration of stores across the country.
- The iPhone Phenomenon: Since its launch in 2007, the iPhone has been Apple’s golden goose. It consistently contributes to over 40% of overall sales. The iPhone’s early generations revolutionized the smartphone industry, and the recent iPhone 14 Pro and 14 Pro Max continue to uphold this legacy, driving year-on-year growth even amidst economic challenges.
- Based on data from the esteemed research firm Counterpoint, Apple’s iPhone shipments to Southeast Asia witnessed an 18% surge in the initial quarter of 2024 compared to the corresponding period in the previous year. Notably, markets in Indonesia and Vietnam exhibited robust demand for iPhones, even as other regions in Southeast Asia approached smartphone market saturation.
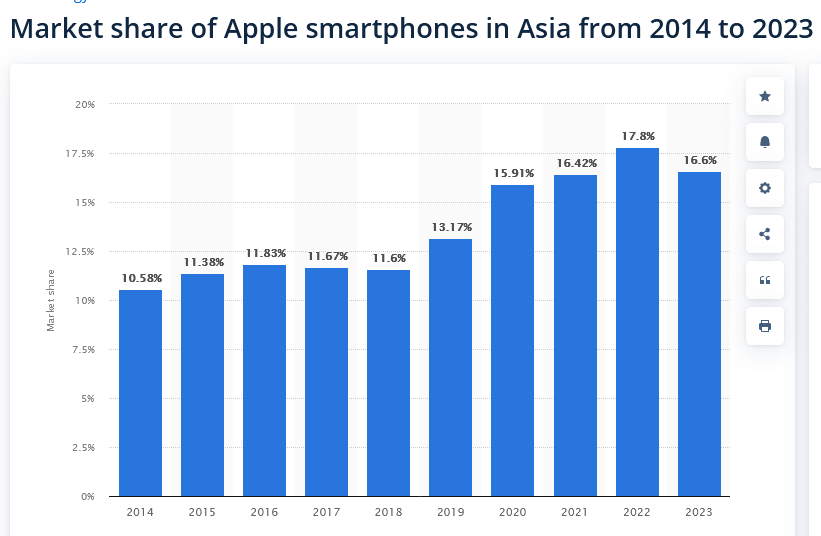
Apple in Asia: An Overview
Take a look at this stats (Apple iPhone Shipments Market Share)
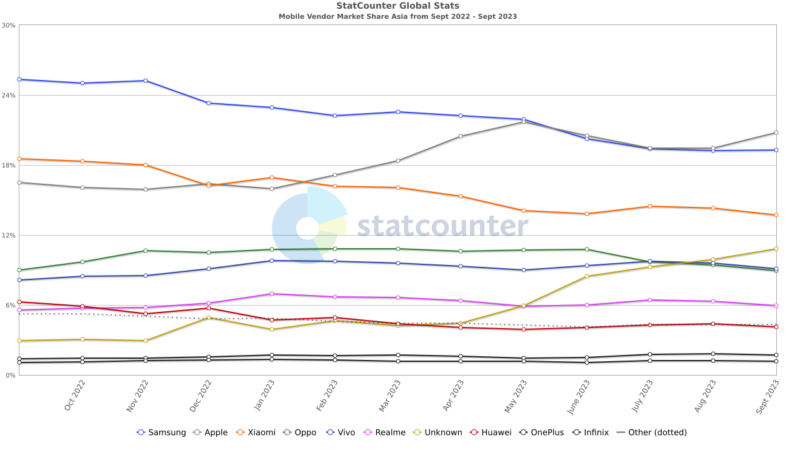
Also, take a look stats at statcounter.com
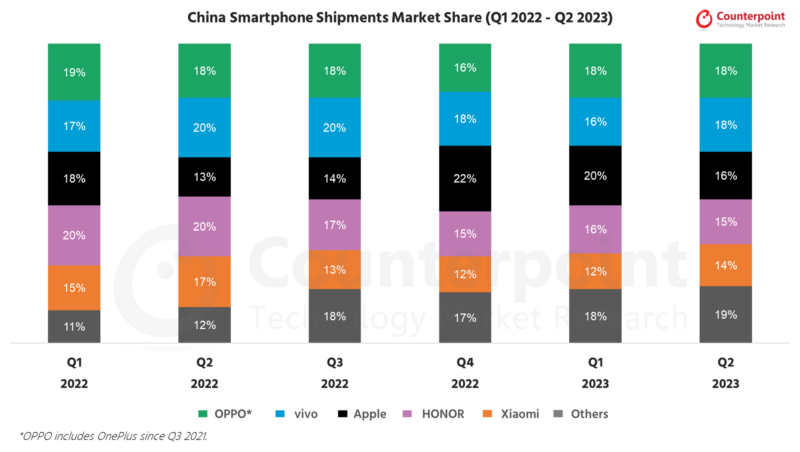
Stats from counterpointresearch.com
Asia, with its vast population and growing middle class, presents a lucrative market for global brands, including Apple. While the exact revenue figures for company in Asia are not explicitly mentioned in the provided source, the significance of regions like Greater China indicates the brand’s strong presence in the continent.
According to AppleInsider, company has become China’s top smartphone vendor for the first time since Q4 2015, with the iPhone getting its highest-ever market share of 23%. This is a significant increase from 2019 when Apple was warning of severe sales problems in China. Counterpoint Research claims that not only has become China’s biggest smartphone brand, but it has also beaten its own record for market share in the country.
It’s a well-acknowledged fact that Asian consumers have a penchant for larger smartphones. A distinct analysis underscores that this preference might have amplified the sales of the iPhone 14 Pro Max models.
As per the 2Q23 data from Omdia’s Smartphone Model Market Tracker, between January and June, Apple’s iPhone 14 Pro Max recorded a global shipment of 26.5 million units, leading the charts across all manufacturers. Following closely, the iPhone 14 Pro secured the second position with shipments of 21 million units.
China in the second quarter 2024. became the biggest iPhone market in the world, overtaking the United States for the first time in history, based on data analyzed by global market research company TechInsights (via The Elec).
Navigating Cultural Nuances: A Case Study
Apple’s journey in China hasn’t been without its challenges. An insightful case study from the Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School titled “Cultural Barriers and Conflict Negotiation Strategies: Apple’s Apology in China” sheds light on how Apple navigated cultural barriers and adopted specific conflict negotiation strategies in the country. The study highlights Apple’s initial missteps in addressing warranty policies and how the company eventually managed to mend its relationship with Chinese consumers through a well-crafted apology and strategic changes.
The Significance of Greater China
Greater China, which includes mainland China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan, is one of its primary markets. The region’s economic growth, coupled with a rising middle class with increasing purchasing power, makes it a hotspot for luxury brands like Apple.
- Cultural Influence: Apple products, especially the iPhone, have become status symbols in many parts of Asia. In cities like Shanghai and Beijing, possessing the latest iPhone model is often seen as a sign of affluence and modernity.
- Competitive Landscape: While Apple enjoys a significant market share in Greater China, it faces stiff competition from local brands like Huawei, Xiaomi, and Oppo. These brands offer high-quality smartphones at competitive prices, challenging Apple’s dominance.
Financial Footprint in China
China stands as a pivotal market, even though the tech giant’s sales in the Greater China region witnessed a dip, reaching a five-year low in 2019. Since its foray into the Chinese smartphone arena in 2010, They experienced a meteoric rise in sales, with revenues amplifying over twenty times in just half a decade, touching a zenith of $58.7 billion by 2015.
According to data from Statista reveals that, in 2015, a quarter of Apple’s global revenue was attributed to China. Yet, the unforeseen COVID-19 pandemic threw a wrench in company operations, impacting both the supply chain and consumer demand.
From a supply perspective, They encountered hurdles in scaling up production after resuming operations post the Chinese New Year celebrations. This led to a ripple effect, causing global shortages in iPhone availability.
On the consumer front, the pandemic’s ramifications were profound, though somewhat localized. The virus’s outbreak compelled Apple to shutter its retail outlets across China temporarily. Even as stores reopened, they reported a stark reduction in footfall, translating to diminished sales.
Unprecedented Earnings in China
In the face of adversities brought about by the pandemic, their impressive performance during the recent festive quarter was fueled, in part, by the enthusiasm surrounding the iPhone 13 in China. This surge came at a time when local giant Huawei grappled with a shrinking market share, a consequence of U.S. trade restrictions.
According to AppleInsider companys revenue from Greater China soared by 60%, setting a new record at $25.8 billion for the quarter that concluded in December 2021. This growth rate surpassed global revenue expansion, which stood at 11%, marking its most sluggish annual growth in over a year. By the fourth quarter of 2022, had carved out a 22% slice of China’s market share, as per data from Counterpoint Research.
Remarkably, they emerged as the sole brand to register positive annual growth in 2020 and has consistently expanded its market presence in China, even amidst a contracting smartphone industry.
Challenges and Opportunities in Asia
Asia is not a monolithic entity. The continent comprises diverse countries, each with its unique cultural, economic, and technological landscape. Navigating this diversity poses both challenges and opportunities for Apple.
- Diverse Consumer Preferences: Asian consumers have varied preferences. While some prioritize brand value and are willing to invest in premium products like the iPhone, others seek value for money and might opt for local brands offering similar features at lower prices.
- Localization Strategies: To cater to diverse Asian markets, company needs to adopt localization strategies. This could include offering region-specific features, collaborating with local influencers, or even adjusting pricing strategies to match local purchasing power.
Le Xuan Chiew, a sharp-eyed tech analyst from Canalys (his study) stationed in Singapore, shared insights with Rest of World, highlighting the role of Asia’s burgeoning young population in Apple’s regional success.
“Traditionally, Apple’s radar has been set on the mature middle-class market. However, the winds of change are blowing, and now they’re casting a wider net, aiming to captivate the vibrant Gen Z and the millennials. The potential avenues for growth and engagement are vast,” Chiew elaborated.
While Apple’s tangible footprint in the region is currently limited to a trio of flagship stores in Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia, they’re not just sitting pretty. The tech giant is innovatively expanding its horizons.
Come May, Apple marked a significant milestone by launching its inaugural online store in Vietnam, a country with over 96 million people and a rapidly growing tech-savvy population. Earlier, in March, Indonesia’s tech powerhouse, Erajaya, a prominent licensed distributor of Apple treasures, unveiled a ritzy Premium Partner store in the bustling streets of Jakarta.
This store promises an immersive experience, rivaling the ambiance of the quintessential Apple Store.
Not to mention, Erajaya’s renowned iBox chain, which is often hailed as Indonesia’s answer to the Apple Store, given its premium service and ambiance.
Market Overview: Apple in Key Asian Countries
India: A Rising Star
India, with its vast population and rapidly growing middle class, is emerging as a pivotal market. While the brand faced initial challenges due to the dominance of budget-friendly smartphones, recent years have seen a surge in company popularity.
The introduction of the iPhone SE, tailored for emerging markets, and the establishment of online store in India have contributed to this growth. Furthermore, their plan to open its flagship retail stores in major Indian cities signals its commitment to this market.
Japan: A Stronghold of Loyalty
Japan has always been a strong market for Apple. The brand’s emphasis on design, quality, and innovation resonates well with Japanese consumers. Apple’s strategic partnerships with major telecom carriers like SoftBank, NTT Docomo, and KDDI have further solidified its presence.
The integration of popular local services, such as Suica for Apple Pay, has made the iPhone an integral part of daily life in Japan.
South Korea: Breaking Barriers
South Korea, home to tech giants Samsung and LG, posed a unique challenge for Apple. However, the brand has made significant inroads in recent years. The opening of Apple’s flagship store in Seoul and the increasing popularity of the iPhone among younger consumers have boosted its market share.
While local brands still dominate, emphasis on privacy, design, and ecosystem gives it a competitive edge.
Indonesia: Tapping into Potential
Indonesia, with its sprawling archipelago and young population, presents a vast opportunity for Apple. While the market is dominated by budget and mid-range smartphones, there’s a growing appetite for premium products among the urban middle class.
Apple’s recent efforts to collaborate with local carriers for bundled offers and its focus on expanding its retail presence indicate its long-term vision for Indonesia.
Apple’s Strategy in Asia: A Closer Look
Success in Asia is not merely a result of its global brand appeal but also a testament to its strategic approach tailored to the Asian market. Let’s delve deeper into the strategies that have propelled Apple to its current stature in the continent.
Collaborations and Partnerships
In Asia, the company has smartly leveraged collaborations and partnerships to enhance its reach and appeal.
- Carrier Partnerships: In countries like Japan and South Korea, Apple has formed partnerships with major telecom carriers. These collaborations often involve exclusive deals or bundled offers, making iPhones more accessible and appealing to the masses.
- Local Integrations: Apple has integrated local services and apps into its ecosystem. For instance, in China, Apple Maps incorporates data from the popular local mapping service AutoNavi, ensuring users get the most accurate and relevant information.
Focus on Retail Experience
Retail strategy in Asia is nothing short of impressive. The brand has invested heavily in creating flagship stores that offer more than just products.
- Architectural Marvels: Stores in Asia are often architectural landmarks. Store in Singapore, floating on Marina Bay, is a testament to commitment to offering unparalleled retail experiences.
- Cultural Integration:They ensure its stores resonate with local culture. In Beijing, the store design draws inspiration from traditional Chinese courtyards, blending modernity with tradition.
Product Localization
Understanding the unique needs and preferences of Asian consumers, company has made efforts to localize its products.
- Language and Features: Devices support a myriad of Asian languages, ensuring seamless user experience. Features like handwriting recognition for Chinese characters make the devices more user-friendly for local consumers.
- Regional Content: The App Store and iTunes have a rich repository of local content, from popular Asian movies to region-specific apps, ensuring users feel a sense of familiarity and relevance.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Prospects
While company has enjoyed significant success in Asia, the road ahead is filled with challenges and opportunities.
Navigating the Competitive Landscape
The Asian smartphone market is fiercely competitive, with local brands vying for a larger market share.
- Rising Local Brands: Brands like OnePlus, Vivo, and Realme are gaining traction, offering high-end features at competitive prices. Company needs to continuously innovate to stay ahead of the curve.
- Balancing Price and Premium: While this is a premium brand, there’s a growing demand for mid-range smartphones in Asia. Apple’s introduction of the iPhone SE series is a step in this direction, but there’s more ground to cover.
Embracing Technological Advancements
Asia is at the forefront of technological advancements, and they needs to be in sync with these trends.
- 5G Integration: With countries like South Korea and China leading the 5G revolution, Apple’s devices need to be 5G-ready to cater to the tech-savvy Asian consumer.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): As AR and VR technologies gain popularity in Asia, Apple’s devices and services need to offer seamless experiences in these domains.
FAQ
How popular is Apple in Asia?
Apple has a significant presence in Asia, with China being one of its primary markets. The brand’s products, especially the iPhone, have become status symbols in many parts of the continent.
Are Apple products popular in Asia?
Yes, Apple products are highly popular in Asia, especially in regions like Greater China, Japan, and South Korea. The iPhone, in particular, has a substantial market share in several Asian countries.
How much does Apple sell in a day?
While the exact daily sales figures can vary, Apple reportedly sells millions of devices globally every day, considering its annual sales figures and product launches.
How many iPhones does Apple sell in China?
Apple has seen a resurgence in its iPhone sales in China, recently capturing its highest-ever market share of 23%. The exact number can vary year by year, but it’s in the millions.
Where are most iPhones sold?
Most iPhones are sold in the United States, followed by regions like Europe and Greater China.
Which country is Apple’s biggest market?
The United States stands as Apple’s most significant market, both in terms of revenue and the number of devices sold.
How popular are iPhones in Europe?
iPhones are highly popular in Europe, with countries like the UK, Germany, and France being significant markets for Apple.
Why is Apple so popular in Japan?
Apple’s popularity in Japan can be attributed to its brand appeal, product quality, and strategic partnerships with major telecom carriers in the country.
Final Words
Company journey in Asia is a testament to its adaptability and understanding of diverse markets. With strategic collaborations, localized offerings, and a keen understanding of consumer preferences, they continue to solidify its presence in this dynamic continent.
References:
- Rest of World. (2024). iPhone Sales in Southeast Asia. Retrieved from https://restofworld.org/2023/iphone-sales-southeast-asia/
- MacRumors. (2024). China Becomes Biggest iPhone Market in Q2 2024. Retrieved from https://www.macrumors.com/2023/08/29/china-biggest-iphone-market-q2-2023/
- CNBC. (2024). Global Smartphone Market to Hit Decade Low; Apple Could Take Top Spot. Retrieved from https://www.cnbc.com/2023/08/17/global-smartphone-market-to-hit-decade-low-apple-could-take-top-spot.html
- Counterpoint Research. Apple iPhone Market Share by Quarter. Retrieved from https://www.counterpointresearch.com/insights/apple-iphone-market-share-quarter/
- DemandSage. iPhone User Statistics. Retrieved from https://www.demandsage.com/iphone-user-statistics/
- Oberlo. Smartphone Market Share Statistics. Retrieved from https://www.oberlo.com/statistics/smartphone-market-share
- StatCounter. Mobile Vendor Market Share in Asia. Retrieved from https://gs.statcounter.com/vendor-market-share/mobile/asia
- Counterpoint Research. China Smartphone Market Share Insights. Retrieved from https://www.counterpointresearch.com/insights/china-smartphone-share/
- Statista. (n.d.). Quarterly Revenue of Apple by Geographical Region. Retrieved from https://www.statista.com/statistics/382175/quarterly-revenue-of-apple-by-geograhical-region/
- Business of Apps. Apple Statistics. Retrieved from https://www.businessofapps.com/data/apple-statistics/
- TechWire Asia. (2024). Apple Sales in China and India Reach New Highs. Retrieved from https://techwireasia.com/2023/08/apple-china-india-sales-new-highs/
- The Wall Street Journal. (n.d.). Apple Faces New Challenge in China as Huawei Releases High-Speed Phone. Retrieved from https://www.wsj.com/tech/apple-faces-new-challenge-in-china-as-huawei-releases-high-speed-phone-beacda95
Related Posts:
- Apple iPhone Sales Skyrocket by 52% in China Making…
- How Much is a Large Blizzard at Dairy Queen?…
- How Much Should I Be Able to Leg Press - Guide for…
- Apple WWDC 2024: iPhone Gets ChatGPT Integration,…
- Does Sonic Take Apple Pay? (Yes, we will explain how)
- How To Unpair Apple Watch: Key Insights and Pro Tips